PCOS Management
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
What is PCOS?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder among women of reproductive age.
In PCOS, eggs in the ovaries do not mature and release. Instead, the eggs form very small cysts in the ovaries. The ovaries may become enlarged, with clusters of fluid-filled cysts on the outside.
The disorder is linked to reduced fertility and an irregular menstrual cycle with light menstrual flow. Women with this disorder may have:
- Difficulty becoming pregnant because they rarely ovulate (release eggs)
- Higher levels of the male hormone androgen
- Problems with insulin production
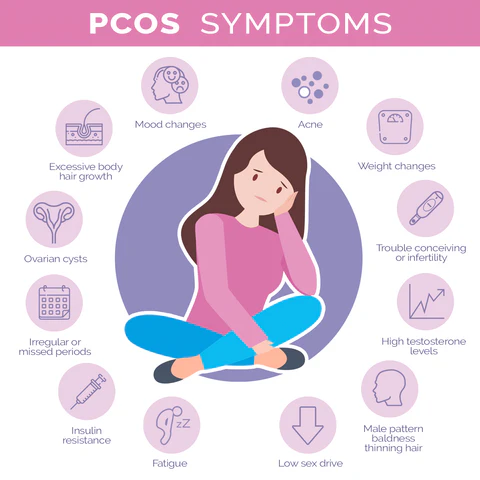
What are the symptoms of PCOS?
If you have PCOS, you may experience symptoms related to increased levels of the male hormone androgen, such as:
- Acne (spots)
- Excess hair growth on the body
- Thinning of the hair on the head (male-pattern hair loss)
- Deepening of the voice
- Decreased breast size
You may also experience one or more of the following symptoms:
- Dandruff
- Infertility
- High cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- Increased insulin levels
- Irregular menstrual periods (e.g. irregular or no menstruation, or long phases of very light or very heavy menstruation)
- Obesity and weight gain
- Oily skin
As the symptoms of PCOS differ between patients and may be related to other illnesses, the condition is often overlooked and undiagnosed.
What causes PCOS?
The exact cause of PCOS is not known, although it is likely to be the result of both genetic and environmental factors.
How do cysts in PCOS form?
Sometimes, it may be difficult to distinguish the difference between PCOS and ovarian cysts because they are related conditions with similar symptoms.
If you have ovarian cysts, the only determinant is if you experience pain in the pelvic area. Most women with PCOS do not experience pain in the pelvic area.
You may have PCOS without ovarian cysts, or you may develop cysts caused by other reasons. If cysts formed in PCOS, it can be due to eggs not being set free for some time. The follicles scattered throughout the ovary can form multiple cysts.
What are the complications and related diseases of PCOS?
As PCOS disrupts hormones, including insulin, you may be at risk for insulin resistance syndrome. Insulin is a hormone that is important for metabolising carbohydrates and maintaining blood sugar levels.
You may face an increased risk of type 2 diabetes, heart disease and stroke at a younger age as women with PCOS are often resistant to insulin.
Other complications may include:
- Elevated lipids and high cholesterol
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Mood swings and depression
- Cancer of the uterus (womb)
- Obstructive sleep apnoea
Meet Our Doctors